The three most important greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4) and nitrous oxide (N 2 O) While carbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas we hear the most about, methane and nitrous oxide have greater global warming potential (GWP)Methane has a GWP of 25 for a 100year period and nitrous oxide has a GWP of 298The AGGI in was 147, which means that we've turned up the warming influence from greenhouse gases by 47% since 1990 It took ~240 years for the AGGI to go from 0 to 1, ie, to reach 100%, and 30 years for it to increase by another 47% In terms of CO 2 equivalents, the atmosphere in contained 504 ppm, of which 412 is CO 2 aloneHowever some gases in the atmosphere, called greenhouse gases, trap escaping thermal energy This causes some of the thermal energy to pass back to the surface This is called the greenhouse

Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
The concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere in 2019 was close to
The concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere in 2019 was close to-The greenhouse effect that has maintained the Earth's temperature at a level warm enough for human civilization to develop over the past several millennia is controlled by noncondensable gases, mainly carbon dioxide, CO 2, with smaller contributions from methane, CH 4, nitrous oxide, N 2 O, and ozone, O 3 Since the middle of the th century, small amounts of manmade gases, Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide is the main longlived greenhouse gas in the atmosphere related to human activities Its concentration reached new highs in 18 of 4078 ppm, or 147% of preindustrial level in 1750 The increase in CO2 from 17 to 18 was above the average growth rate over the last decade



Annual Ghg Index Aggi
"There is no sign of a slowdown, let alone a decline, in greenhouse gases concentration in the atmosphere despite all the commitments under the Paris agreement on climate change," said WMOEffects of increased greenhouse gases The growing concentrations of humangenerated GHGs have resulted in an increased absorption, largely in the lower atmosphere, of the heat radiated from Earth's surface, causing an increase in the global (land and ocean) mean surface temperature of 085 ± 0 °C from 10 to 12 ( Stocker et al 13a The graphs show monthly mean carbon dioxide measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii The carbon dioxide data on Mauna Loa constitute the longest record of direct measurements of CO 2 in the atmosphere They were started by C David Keeling of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in March of 1958 at a facility of the National Oceanic and
When Earth first formed, Earth's atmosphere may have contained more greenhouse gases and CO 2 concentrations may have been higher, with estimated partial pressure as large as 1,000 kPa (10 bar ), because there was no bacterial photosynthesis to reduce the gas to411 Sources of Greenhouse Gases 243 412 Atmospheric Chemistry and Feedbacks 245 413 Trace Gas Budgets and Trends 246 414 Atmospheric Lifetimes and TimeScales 247 42 Trace Gases Current Observations, Trends and Budgets 248 421 NonCO 2 Kyoto Gases 248 4211 Methane (CH 4) 248 4212 Nitrous oxide (N 2O) 251 4213Based on greenhouse climate models and other considerations, it is possible that atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations may double from their late 1700s level of 275 ppmv by the years 30–50 By 15, atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations had surpassed 400 ppmv for the first time in 800,000 years
Concentrations are expected to stay above 400 ppm for many generations, because CO 2 can remain in the atmosphere for hundreds of years CO 2 is a longlived greenhouse gas responsible for roughly 65 percent of the total warming effect caused by greenhouse gases globally Why is this indicator important?Greenhouse Gases and Temperature A greenhouse gas (GHG) is any gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation in the thermal infrared range These are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect, which results in increased temperatures on Earth The greenhouse effect occurs as the gases reach Earth's surfaceThe naturally occurring gases in the atmosphere, showing where the highest concentration of gases are and the percentages of each accurately The greenhouse gases in the atmosphere (rememberthese are also naturally occurring – just in a harmful percentage) Each continent and the areas of highest global emission within The Ozone Hole




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly
Global warming "Greenhouse effect" Since the industrial revolution, the concentration of greenhouse gases has been steadily growing There is now a reasonable consensus that this will produce an increase in the heat trapped in the atmosphere and consequently a global climate change The more likely changes are shifting of climatic zones and aAtmosphere, which in turn depends upon the input of solar radiation and the atmospheric abundances ot ladiatively active trace gases (1 e , greenhouse gases), clouds and aerosols Since the industrial revolution the atmospheric concentrations of several greenhouse gases, i e , carbon dioxide (CO2) methaneThe increase in atmospheric CO 2 concentration since 1860, which is approximately the beginning of the fossil fuel era, has been slightly more than 60 percent of the concentration that would be in the atmosphere if all the fossil fuel emissions had remained in the atmosphere The results of most models of the oceanatmosphere carbon system are consistent with this approximate 60



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




All Scenarios Assume Continued Growth In Atmospheric Levels Of Download Scientific Diagram
Human activities and the greenhouse effect Human activities are increasing the amount of some greenhouse gases in the atmosphere For example farming cattle releases methaneHow can it be so important in global warming if it's such a small percentage?Carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases can absorb and release infrared radiation and alter that balance The longterm increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is the primary cause of the observed longterm increase in global temperature The warming effect of greenhouse gases was first predicted in the 19th century



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
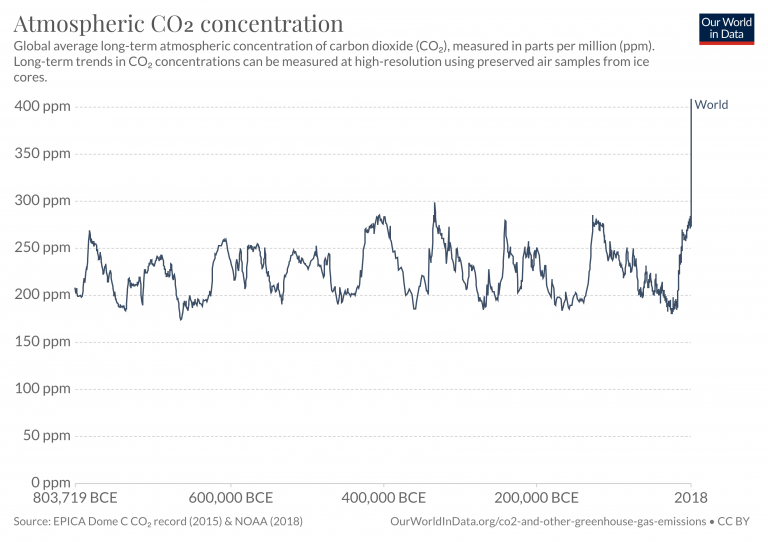



Atmospheric Concentrations Our World In Data
The enhanced greenhouse effect What has scientists concerned now is that over the past 250 years, humans have been artificially raising the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere at an everincreasing rate, mostly by burning fossil fuels, but also from cutting down carbonabsorbing forestsIn order, the most abundant greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are Water vapor ( H 2O) Carbon dioxide ( CO 2) Methane ( CH 4) Nitrous oxide ( N 2O) Ozone ( O 3) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Hydrofluorocarbons (includes HCFCs and HFCs)8 rows Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, For most of the past 800,000 years—much longer than human civilization has existed—the concentration of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere was between about 0 and 280 parts per million (In otherThe greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can both absorb and reradiate much of the outgoing heat energy The atmospheric concentrations of some greenhouse gases are being affected directly by human activities namely carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3 ), and synthetic gases, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrofluorocarbons




Atmospheric Methane Wikipedia



Www Pbl Nl Sites Default Files Downloads Pbl Trends In Global Co2 And Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions 19 Report 4068 Pdf
The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor,The concentration of greenhouse gases can make the atmosphere essentially opaque in a particular band If the atmosphere absorbs 100 percent of the radiation in a band the absorption will not be increased when additional greenhouse gases are added The atmosphere would then be said to be saturated in that particular frequency band However fullAnthropogenic greenhouse gases Since the start of the Industrial Revolution in the mid18th century, human activities have greatly increased the concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere Consequently, measured atmospheric concentrations of CO 2 are many times higher than preindustrial levels
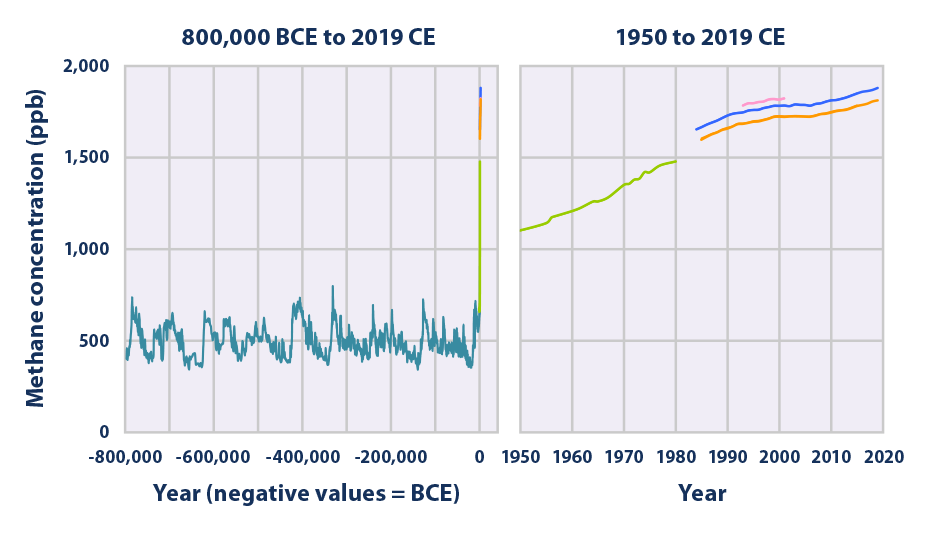



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
Greenhouse gases are gases in the earth's atmosphere that trap heat During the day, the sun shines through the atmosphere, warming the earth's surface At night, earth's surface cools, releasing heat back into the air But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere That's what keeps the earth's temperature at Greenhouse gases differ in the way they affect the climate system In order to sum the effects of the individual greenhouse gases and other forcing agents in the atmosphere, the socalled 'greenhouse gas equivalent concentration' has been defined This is the concentration of CO 2 that would cause the same amount of radiative forcing as aI am often asked how carbon dioxide can have an important effect on global climate when its concentration is so small – just 0041 percent of Earth's atmosphere




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
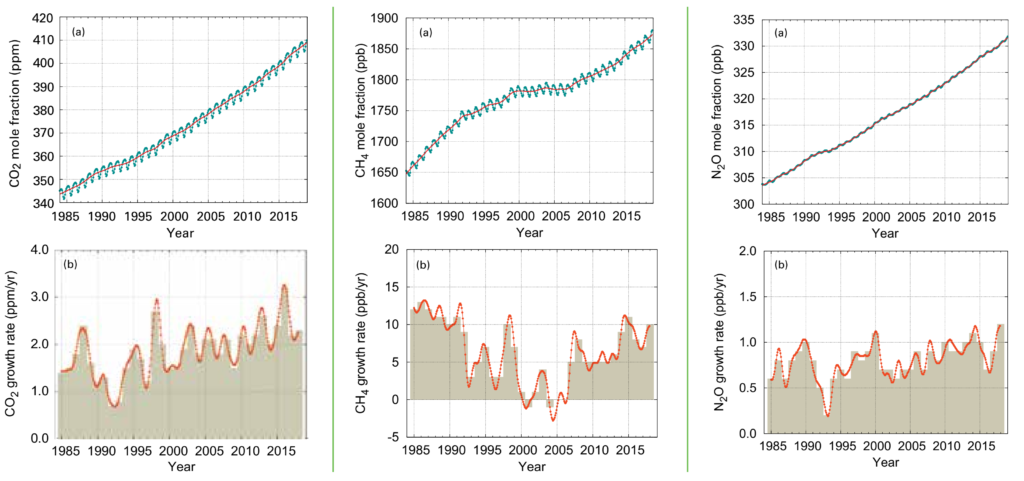



Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reached Yet Another High In 18 Desdemona Despair
Key Points Global atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and certain manufactured greenhouse gases Historical measurements show that the current global atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous Carbon dioxide concentrations have increasedThe Negatives Well, the surge in the concentration of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere is undeniable, and we have already seen some critical changes in the climate due to the greenhouse effect Some disadvantages of the greenhouse effect are quite evidentGoing from the level of carbon dioxide in the air before the industrial revolution, 280 parts per million by volume (280 ppm) to twice that, 560 ppm, and letting the climate come into balance will warm the surface by about 3 C How much more carbon dioxide must be added to the atmosphere to warm the surface by another 3 C?
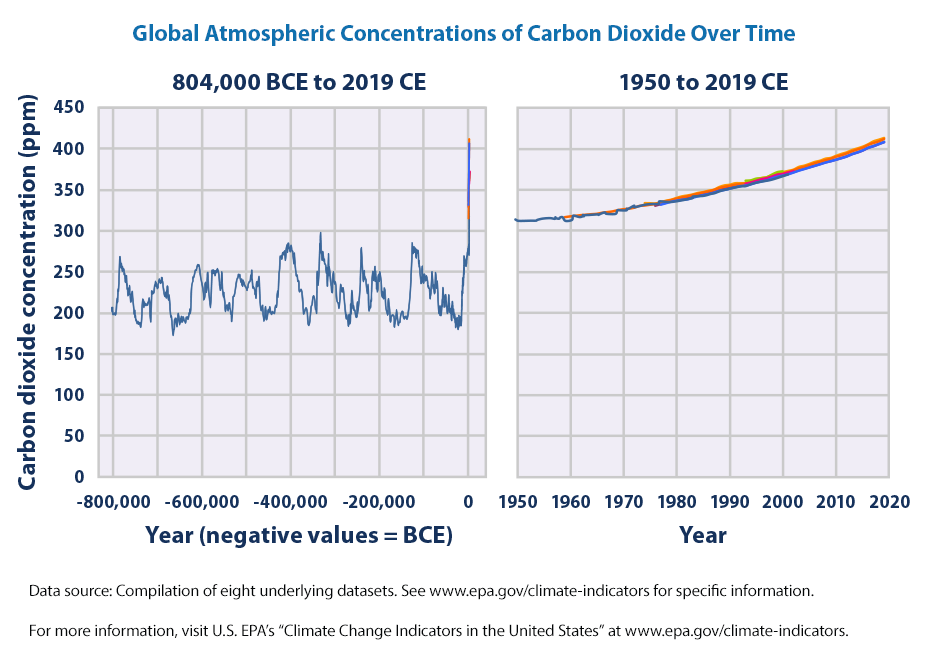



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Whole Atmosphere Mean Ghg Concentration Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite
Carbon dioxide is the main longlived greenhouse gas in the atmosphere Concentrations reached 4055 ppm in 17, 146% of the preindustrial era (before 1750) The increase in The concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere hit a record high in 18 and will lead to more extreme weather, the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) has said The UN agency's Greenhouse Gas Bulletin is one of a series of studies to be published ahead of a UN climate change summit being held in Madrid next week, and is expected to guide discussions there The greenhouse gasses present in the atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane,




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization



3
Comparing greenhouse gases All greenhouse gases absorb energy, but different gases have different effects on warming Carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide remain in the atmosphere for long enough to allow them to mix together As a result, the gas concentrations are about the same around the globe, regardless of the source or location of the emissionsNoun phenomenon where gases allow sunlight to enter Earth's atmosphere but make it difficult for heat to escape greenhouse gas Noun gas in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and ozone, that absorbs solar heat reflected by the surface of the Earth, warming the atmosphere The global average atmospheric carbon dioxide in 19 was 4098 parts per million ( ppm for short), with a range of uncertainty of plus or minus 01 ppm Carbon dioxide levels today are higher than at any point in at least the past 800,000 years Global atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations (CO 2) in parts per million (ppm) for the past



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Those Who Worry About Co2 Should Worry About Methane Too The Economist
Greenhouse Gases wwwepagov/climateindicators Updated August 16 2 About the Indicator This indicator describes concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere It focuses on the major greenhouse gases that result from human activities For carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and halogenated gases, recent measurements come from Carbon dioxide is the main longlived greenhouse gas in the atmosphere related to human activities Its concentration reached new highs in 18 of "There is no sign of a slowdown, let alone a decline, in greenhouse gases concentration in the atmosphere despite all the commitments under the Paris agreement on climate change," said WMO




If Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases Are Reduced How Quickly Do Their Concentrations In The Atmosphere Decrease Weadapt Climate Change Adaptation Planning Research And Practice
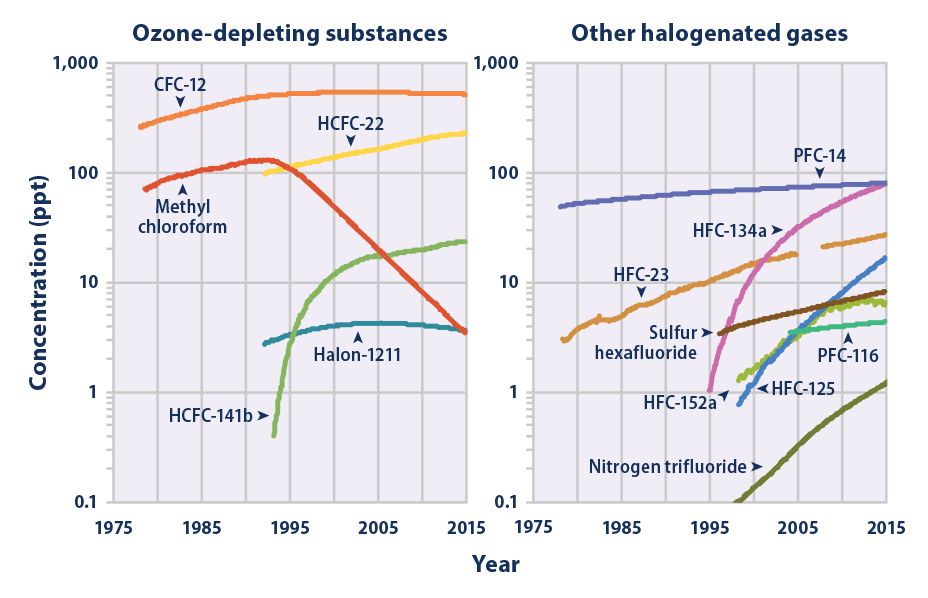



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
"The Greenhouse Gas Bulletin shows that, far from falling, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere actually increased last year at the fastest rate for nearly 30 years," said MichelGreenhouse gases in the atmosphere, including water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, absorb heat energy and emit it in all directions (including downwards), keeping Earth's surface and lower atmosphere warm Adding more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere enhances the effect, making Earth's surface and lower atmosphere The concentration of carbon dioxide, a product of burning fossil fuels that is the biggest contributor to global warming, surged from 4055 parts per million in 17 to 4078 ppm in 18 This exceeded the average annual increase of
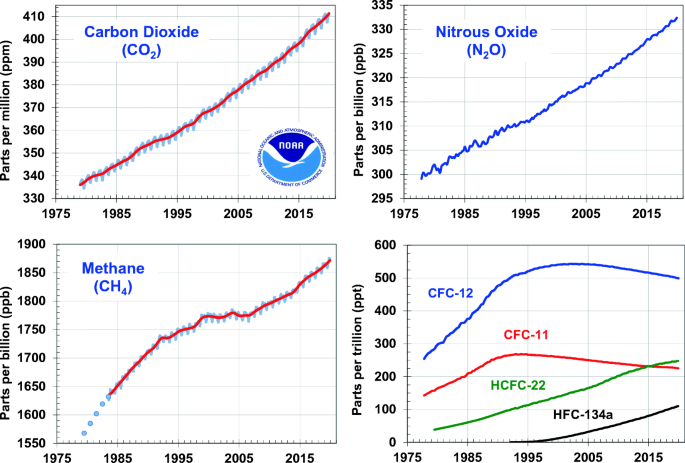



Observations Of Greenhouse Gases As Climate Indicators Springerlink
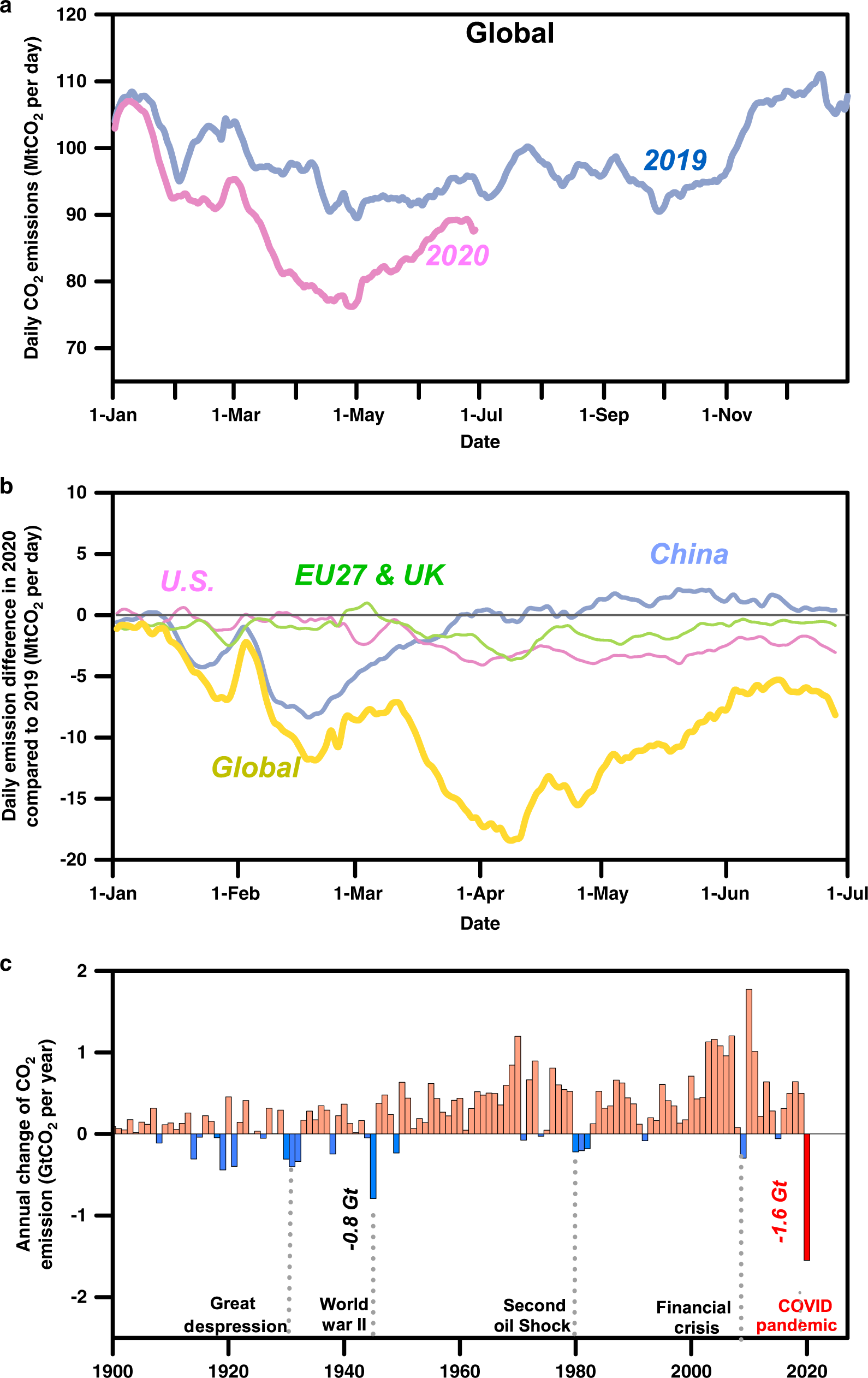



Near Real Time Monitoring Of Global Co2 Emissions Reveals The Effects Of The Covid 19 Pandemic Nature Communications
Measurements of greenhouse gases (GHGs), whether performed in the atmosphere, or over terrestrial or marine ecosystems, have led to a fundamental understanding of the Earth System during the last century Nevertheless, we still do not fully understand global greenhouse gasAtmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations Concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere have risen over time Levels are expected to remain highfor many generations Rising global temperatures are directly linked to increased concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere These gases warm the Earth's surface by trapping heat Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb solar radiation in the form of heat, therefore heating up the Earth Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would have a temperature of °C However, human activity is increasing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, meaning that more and more heat is being absorbed, which in turn drives things such as global




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency
Carbon dioxide controls the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere and thus the size of the greenhouse effect Rising carbon dioxide concentrations are already causing the planet to heat up At the same time that greenhouse gases have been increasing, average global temperatures have risen 08 degrees Celsius (14 degrees Fahrenheit) since 10 Reader question I heard that carbon dioxide makes up 004 percent of the world's atmosphereNot 04 percent or 4 percent, but 004 percent!




If Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases Were Stopped Would The Climate Return To The Conditions Of 0 Years Ago Royal Society
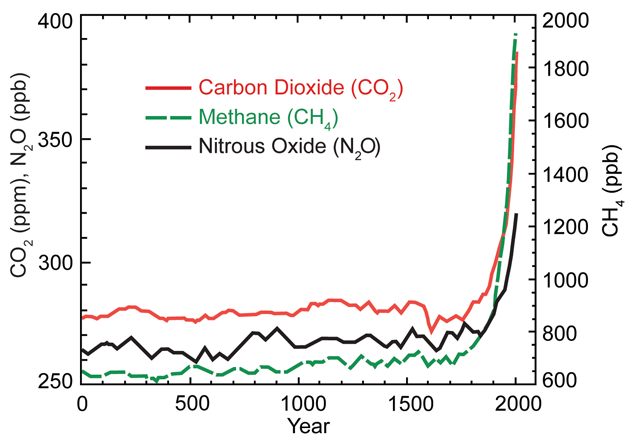



Rocky Rex S Science Stuff 19




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
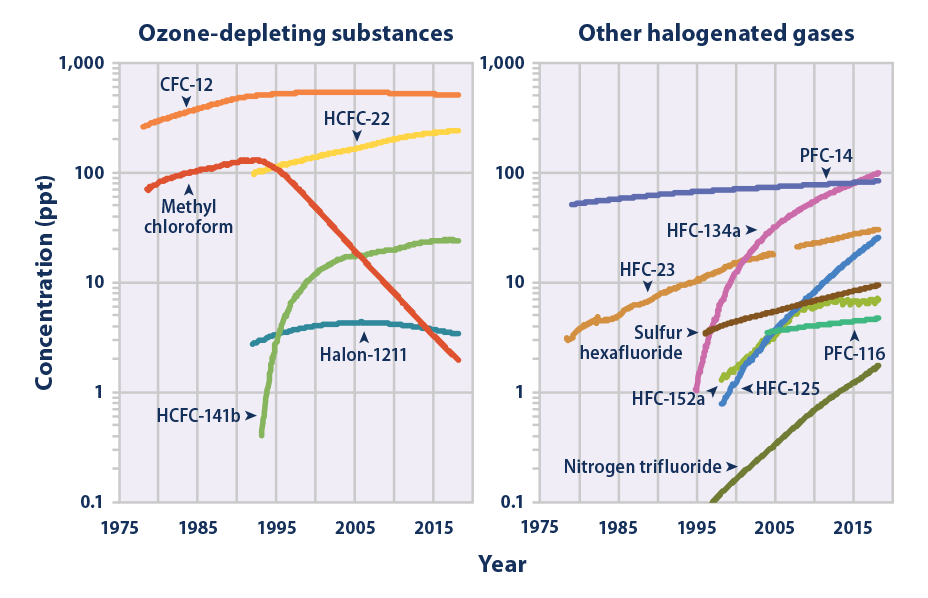



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Greenhouse Gas Basics 148 Msu Extension
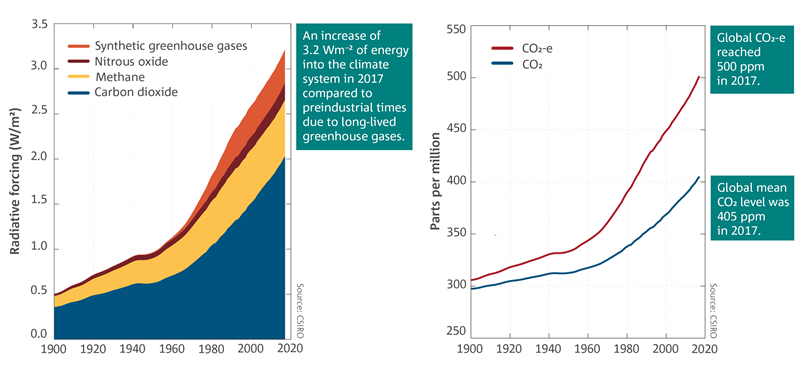



Greenhouse Gases Csiro




Warming Influence Of Greenhouse Gases Continues To Rise Noaa Finds Welcome To Noaa Research




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus




Atmospheric Concentrations Of Important Long Lived Greenhouse Gases Download Scientific Diagram
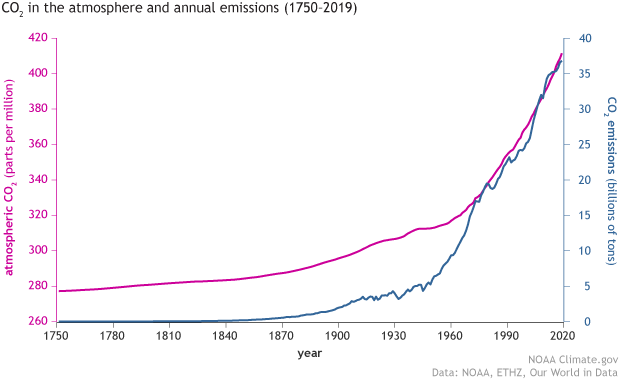



Climate Change Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Noaa Climate Gov



1
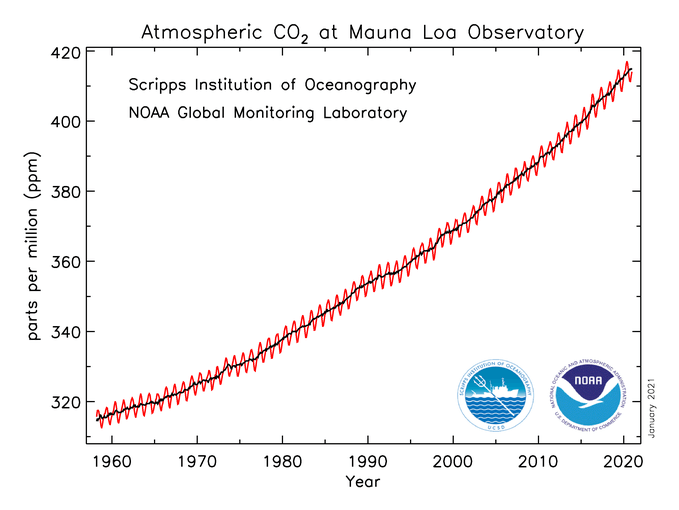



Main Greenhouse Gases Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
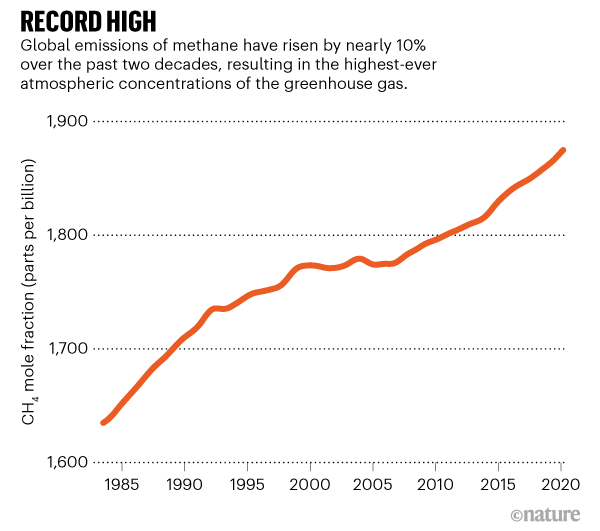



Global Methane Levels Soar To Record High
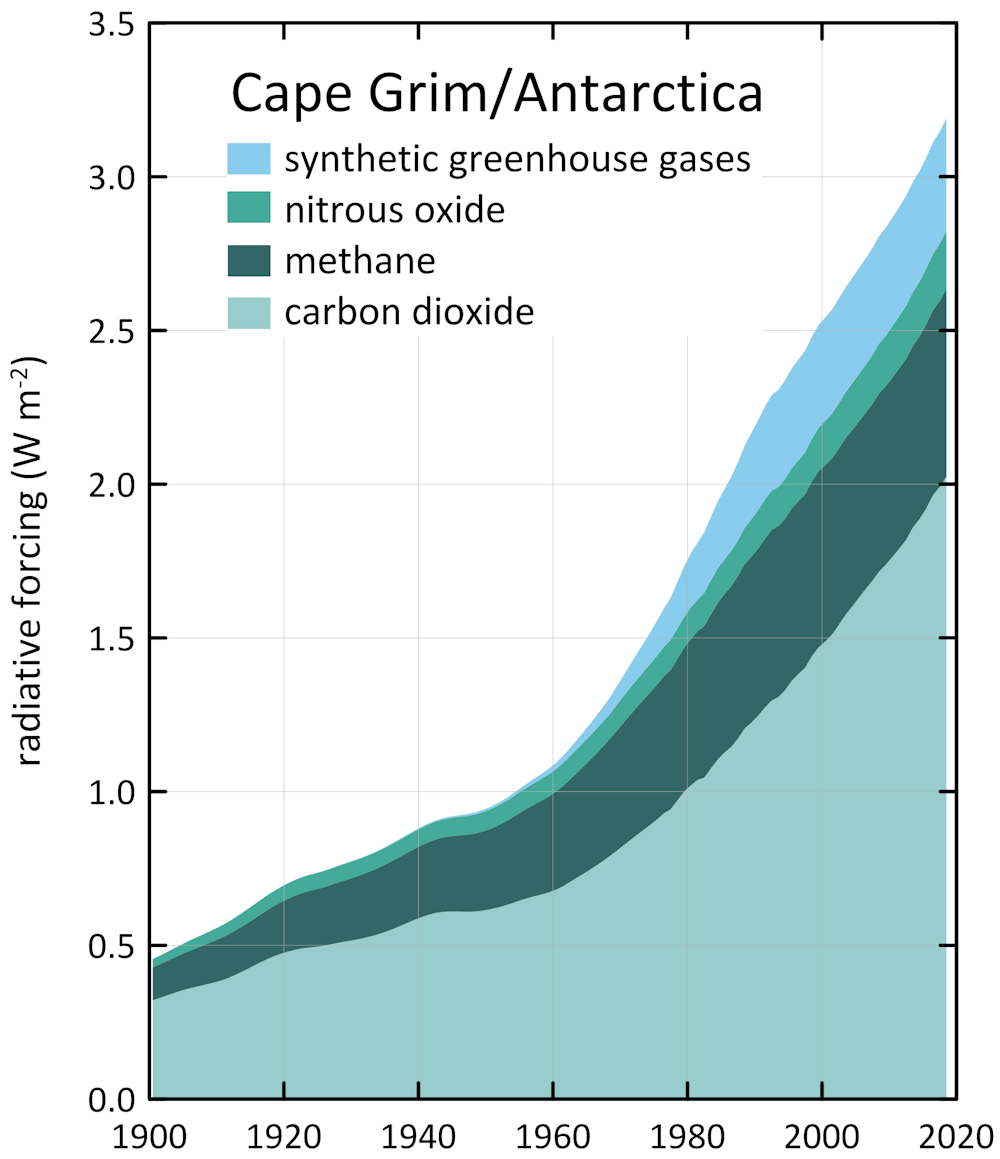



Why There S More Greenhouse Gas In The Atmosphere Than You May Have Realised




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Copernicus




Global Warming Radiative Forcing Britannica



Q Tbn And9gcs3 Vn3xnwnq9ifctpyrsa2ofh2ymxfw2rxlcy7frr77uflqr Usqp Cau
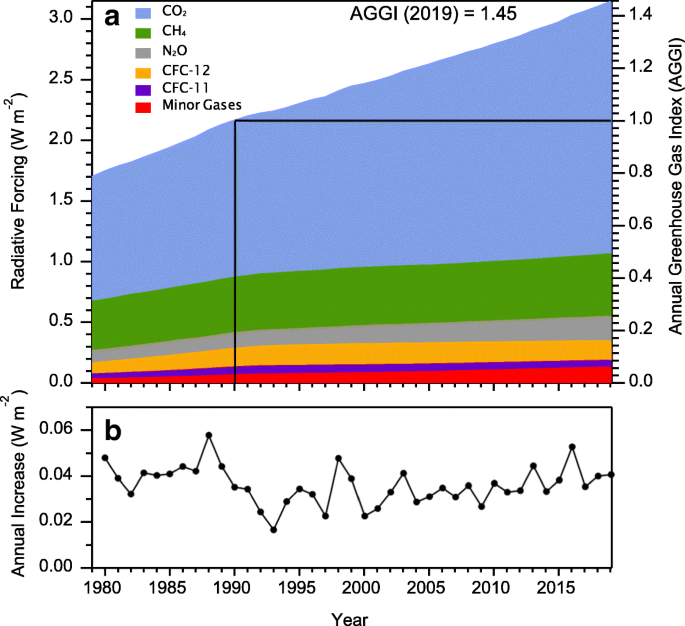



Observations Of Greenhouse Gases As Climate Indicators Springerlink



Q Tbn And9gcrzcnvavdxpfcy 6emwgu68k Cpismnapt0frk Uehnjqqnaxwn Usqp Cau




Far From Turning A Corner Global Co2 Emissions Still Accelerating Inside Climate News
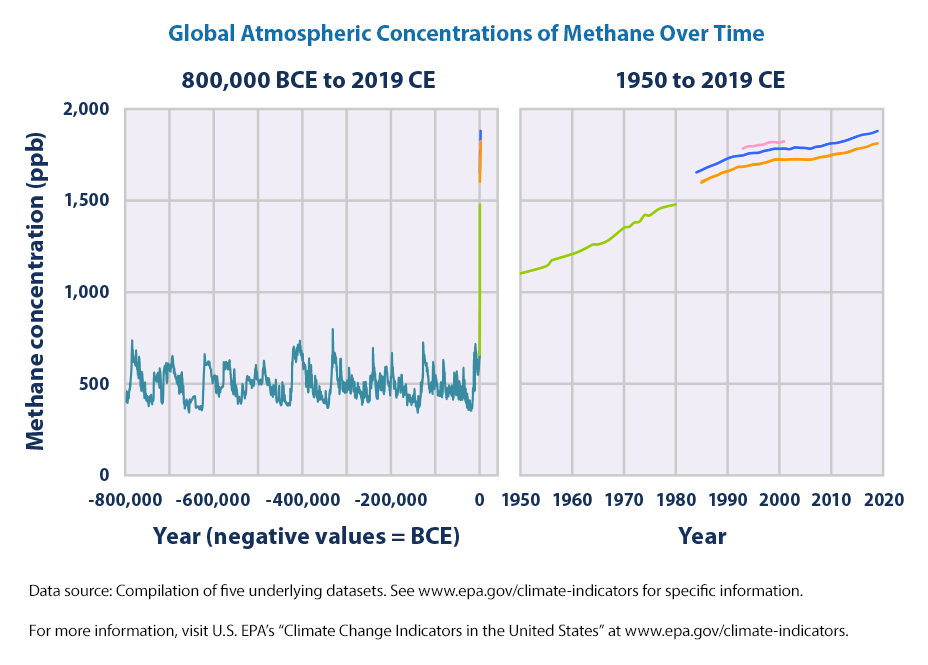



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Annual Ghg Index Aggi




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
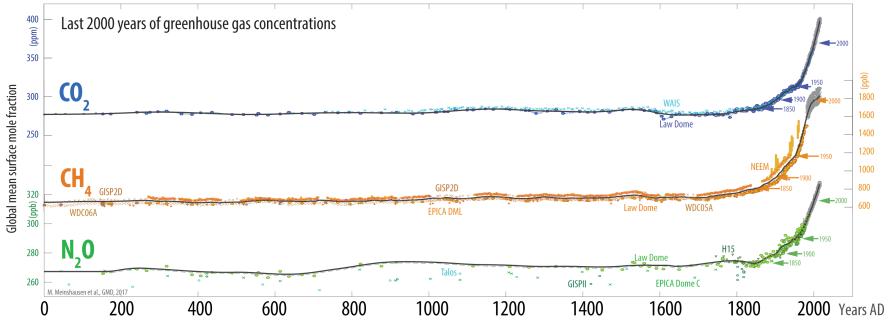



Key Greenhouse Gases Higher Than Any Time Over Last 800 000 Years Pursuit By The University Of Melbourne




Changes Since The Industrial Revolution American Chemical Society




Easing Off The Greenhouse Gas Science Mission Directorate



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
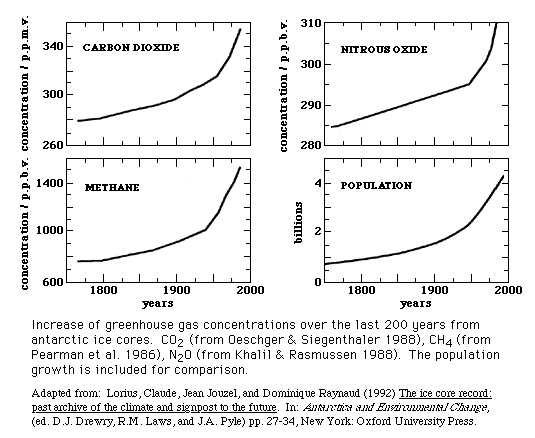



V1003 Science And Society Sources And Impacts Of Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record World Meteorological Organization



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Wxshift



Representative Concentration Pathway Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Copernicus




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Hit New High Un




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Surge To New Record World Meteorological Organization




Atmospheric Concentrations Of The Three Main Greenhouse Gases Carbon Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus



Belching Ruminants A Minor Player In Atmospheric Methane Stories Nafa



The Greenhouse Effect



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming
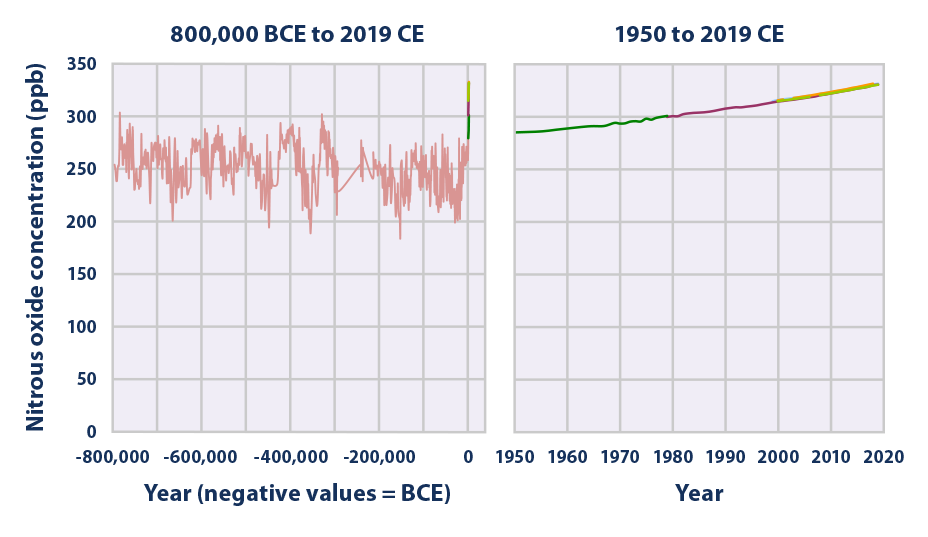



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Gmd The Shared Socio Economic Pathway Ssp Greenhouse Gas Concentrations And Their Extensions To 2500




Atmospheric Concentration Of The Major Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gases Download Scientific Diagram



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
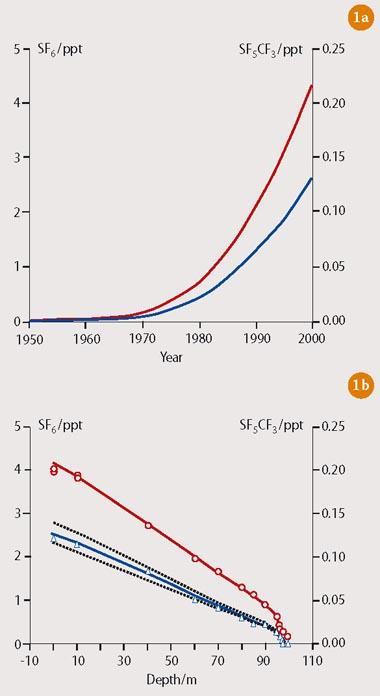



Cf3sf5 A Super Greenhouse Gas Feature Rsc Education




Influence Of Greenhouse Gases To Global Warming On Account Of Radiative Forcing Intechopen
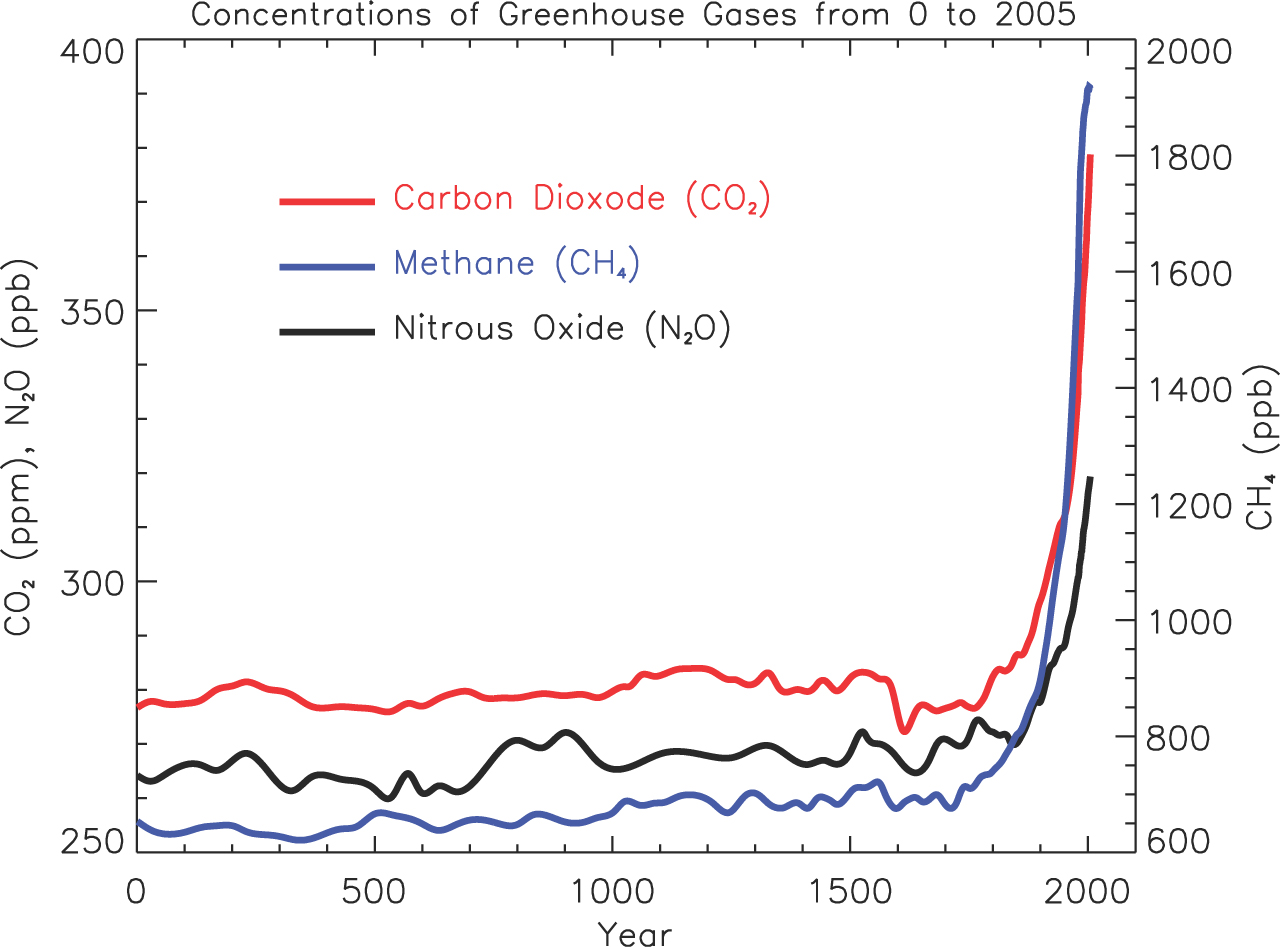



A World Of Images



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature




Climate Change Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Noaa Climate Gov




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization



State Of The Climate Bureau Of Meteorology




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization




Recent Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Download Table




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization




This Graph Shows The Increase In Greenhouse Gas Ghg Concentrations In Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
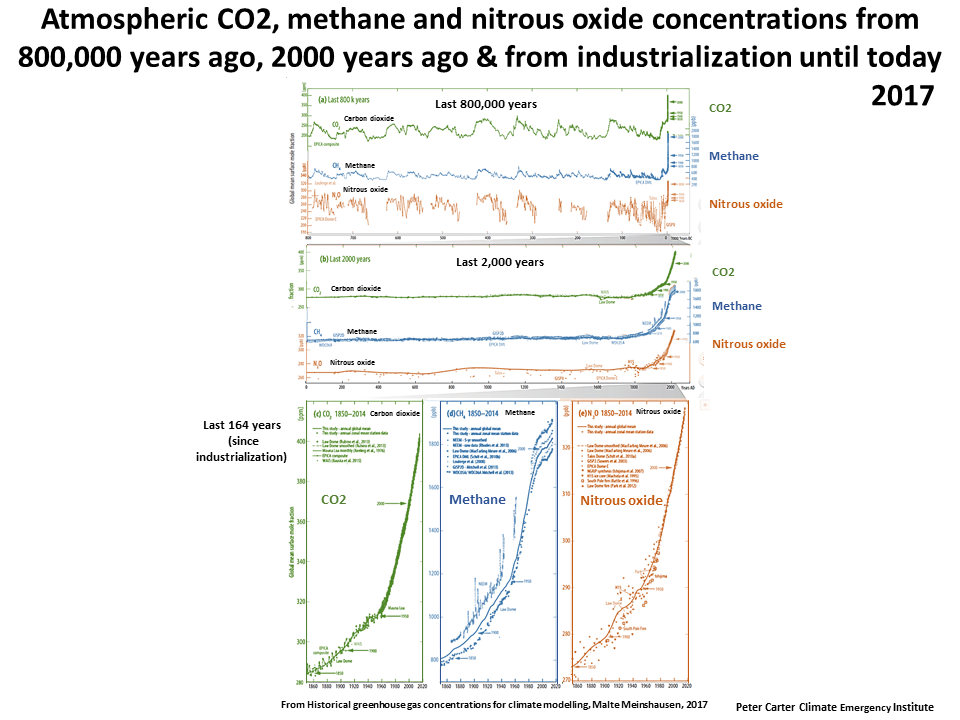



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gases
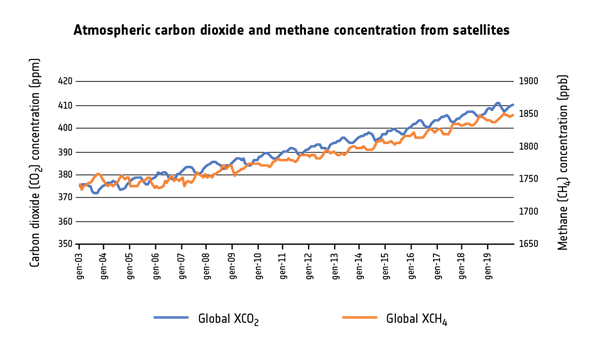



Climate Change The Evidence From Space




Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
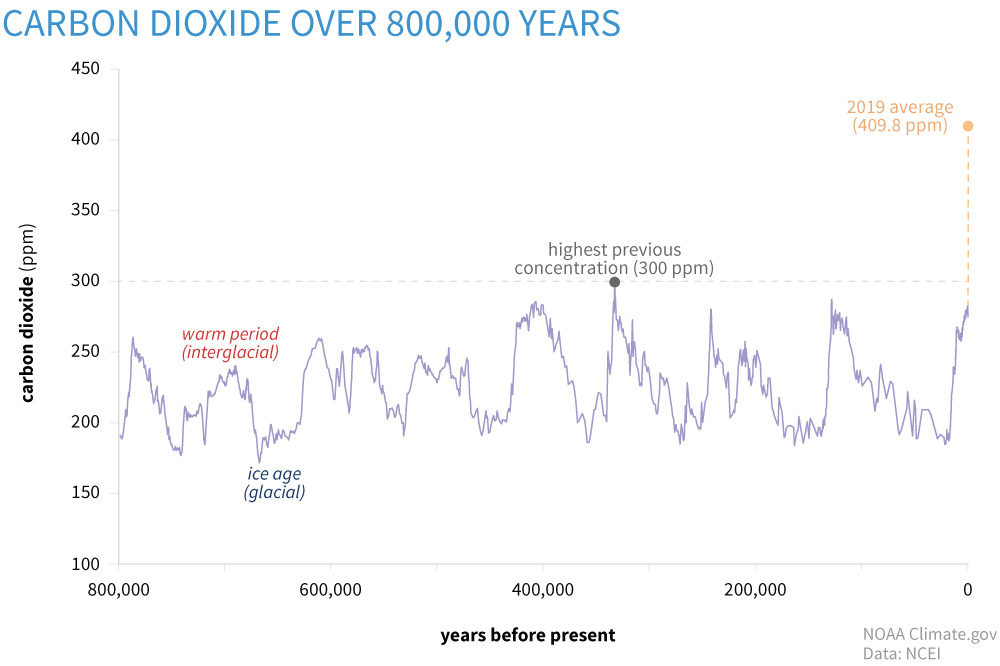



Climate Change Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Noaa Climate Gov



Atmospheric Concentrations Fluorocarbons



Annual Ghg Index Aggi



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Www Pbl Nl Sites Default Files Downloads Pbl Trends In Global Co2 And Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions 19 Report 4068 Pdf
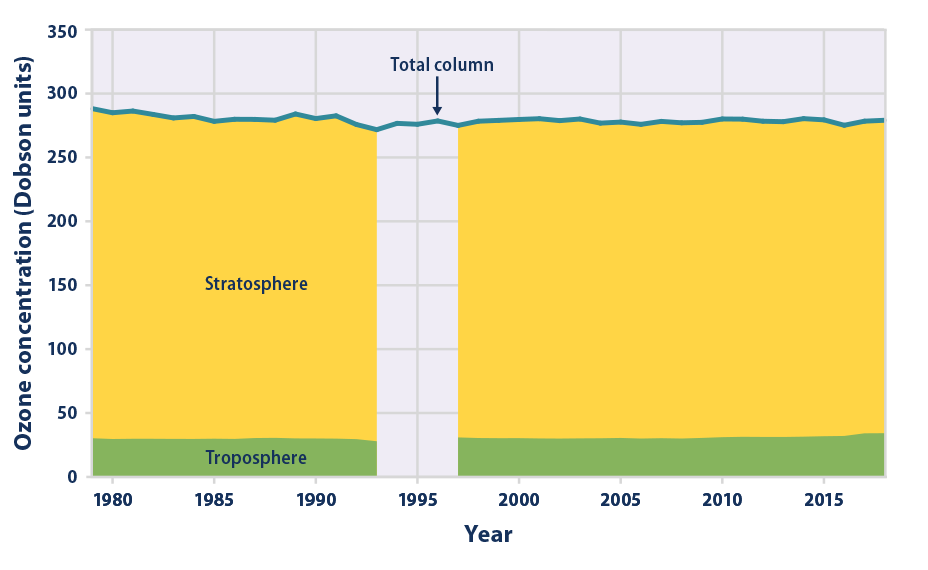



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Changes In Concentration Of Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Other Greenhouse Gases And Aerosols



大気観測装置 開発から搭載までの経過


